
#Does sas have the caret symbol code
There are two ways to "comment out" a line of text or code in a SAS program: A well-commented program helps you to remember what your thought process was when you first created the program, and helps other users decipher what your program is doing. Comments make a written program more understandable by documenting what the program is doing (or should be doing), and why. Here is an example of how a typical program would be set up, making use of indentations and spacing, one statement per line, and capital letters.Ī comment is a line or block of text that SAS ignores during the execution of a program.
Most SAS programmers use capital letters, indentations, and spacing in a way that makes it easier for themselves and other users to read and understand their program.
You know you have properly typed text values when SAS changes the color of the words into a purplish-pink color. You will need to enclose text in quotation marks or apostrophes if you need to reference values of a character variable, reference a file directory, or assign a title to your output, to name a few example. It doesn’t matter which one you choose, but be sure each text block starts and ends with the same one. SAS recognizes text as long as it is enclosed in quotation marks ( "text") or apostrophes ( 'text').

Omitting the semicolon is the most common mistake new users make. This generally corresponds to every line ending in a semi-colon, but sometimes your commands or statements will be more than one line and a semicolon is only necessary at the end of the statement. SemicolonsĮvery statement must end with a semicolon.
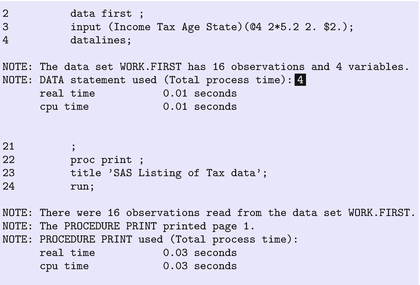
There are some conventions of SAS syntax that new users should know before getting started. SAS syntax is the set of rules that dictate how your program must be written in order for SAS to understand it. You can save your program so that it can be edited and reused after it’s written.
#Does sas have the caret symbol series
A SAS program is written in the Editor window and contains a series of statements that tell SAS what to do (e.g., import a dataset, give a frequency count of a variable).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
